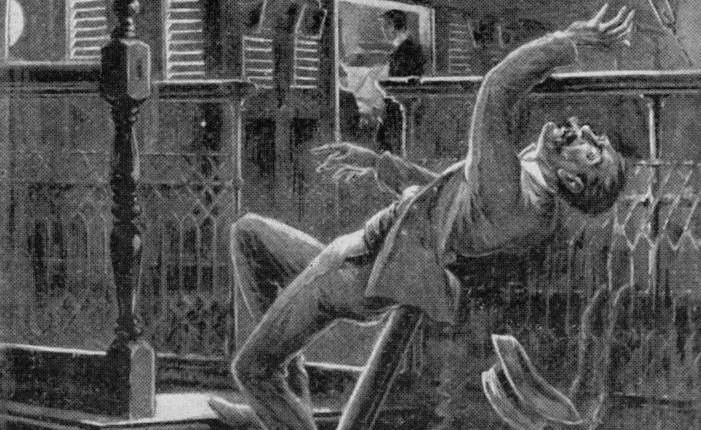Copyright 2009 by Gary L. Pullman
It is not generally known, but Sir Winston Churchill, the prime minister of Great Britain during World War II, not only painted landscapes and other paintings, but he also wrote short stories, one of which, “Man Overboard” (1899), is the subject of this post.

Sir Winston Churchill
The story is similar, in some ways, to Stephen Crane’s short story, “The Open Boat,” and to the 2003 film Open Water. Perhaps we shall consider these other stories in future articles.
Churchill’s first short story, “The Open Boat,” appeared in this magazine.
In “Man Overboard,” the anonymous protagonist falls overboard from a “mail steamer” that is sailing east through the Red Sea. It is “a little after half-past nine,” the omniscient narrator informs us, “when the man fell overboard.” He’d left the ship’s “companion-house,” where a concert was in progress, to “smoke a cigarette and enjoy a breath of the wind,” when, leaning back upon a railing which gave way, he “fell backwards into the warm water of the sea amid a great splash.”
The story’s second paragraph describes sights, sounds, and tactile sensations that could be discerned from either the deck or the sea itself, and is, therefore, ambiguous as to the man’s whereabouts. Is he still aboard at this time or has he already fallen overboard? The story shifts back and forth, between the interior and the deck of the ship and the water:
The night was clear, though the moon was hidden behind clouds. The warm air was laden with moisture. The still surface of the waters was broken by the movement of the great ship, from whose quarter the long, slanting undulations struck out like feathers from an arrow shaft, and in whose wake the froth and air bubbles churned up by the propellers trailed in a narrowing line to the darkness of the horizon.
The painter’s eye is discernable in the writer’s imagery; Churchill paints a clear picture, terrible in its simplicity. This paragraph is an example of something that literature can do that would be difficult, if not impossible, for film to accomplish. Its ambiguity provides a double perspective, allowing the reader to see and hear and feel the sky, the air, and the water both from the ship and from the sea at the same time. These shifts between the cozy comfort of the ship and “the blackness of the waters” heightens the horror of the story, producing uncertainty as to the man’s location and representing both the possibility of his safety as well as that of his peril.
Although his fall produces “a great splash,” the noise is not enough, over the distance and the sound of the musical instruments, to be heard, and the concert to which he’d been listening, mere moments ago, with pleasure now becomes something of a mocking and terrible reminder of his separation from the ship and its passengers and crew. Separated from the group, he is all alone in the sea. His absence goes unnoticed as the band plays “a lively tune,” the first verse of which is, rather ominously, “accompanied” by “the measure pulsations of the screw,” or ship’s propeller.
Churchill employs the passive voice throughout much of his story, an unusual technique, which heightens the impersonal character of the sea and the shock of the protagonist who has fallen overboard. His actions are automatic, desperate, and “inarticulate.” His terror has robbed him of his ability to think or to speak in an articulate fashion:
For a moment he was physically too much astonished to think. Then he realised he must shout. He began to do this even before he rose to the surface. He achieved a hoarse, inarticulate, half-choked scream. A startled brain suggested the word, “Help!” and he bawled this out lustily and with frantic effort six or seven times without stopping. Then he listened.
He listens, but he hears only the chorus of the song that the ship’s distant passengers and crew sing, their very singing proof that they are as unaware of the man overboard as if he didn’t exist.
Nor does the sea respond to his desperate cries for help. Nature has no heart, no mind, no soul; it is utterly indifferent, so to speak, to the fate of the man overboard, and he is more acted upon, both by nature and his own instinctive drives, than he is active. Free will means little when one is alone in an impersonal ocean.
Technology, as represented by the mail steamer--a ship that carries human correspondence, representing connection and communication among men and women--is of no avail in the world of nature. The narrator, stripped, as it were, of humanity’s technological capabilities and armor, is mere flotsam, no better or more valuable than any other detritus afloat upon the seas. Men may value themselves and one another; the sea, a synecdoche of nature as a whole, does not, a theme that “The Open Boat” and Open Water share with Churchill’s story and which is well expressed by Crane in a short poem, “A Man Said to the Universe,” that could stand as the epigraph to any of these stories:
A man said to the universe:
"Sir I exist!"
However," replied the universe,
"The fact has not created in me
A sense of obligation."
As the ship continues to steam away from the man, the music and the vessel’s lights dim, the ship seeming to get smaller and smaller in the distance, heightening the horror of the protagonist's situation and the terror he feels, even as the increasing silence and the lengthening gap emphasizes his aloneness, his vulnerability, and his desperation:
The chorus floated back to him across the smooth water for the ship had already completely passed by. And as he heard the music a long stab of terror drove through his heart. The possibility that he would not be picked up dawned for the first time in his consciousness.
As he hears, again, the chorus, he screams again for help, “now in desperate fear,” only to hear, as if it is mocking him, the chorus’ refrain, its “last words drawled out fainter and fainter.”
The instinct for self-preservation is strong within him--at first; however, his desire to live soon weakens as, after setting “out to swim after it [the ship] with furious energy, pausing every dozen strokes to shout long wild shouts,” he stops, as “full realisation” comes to him that he is “alone--abandoned.” This “understanding” of his predicament, the narrator remarks, causes his brain to reel, and he has a second burst of determination to save himself, praying, this time, rather than shouting. Instead of depending upon his fellow human beings for assistance, he has turned to God, pleading for divine assistance.
Almost immediately, as if Churchill intends his story’s theme to be that God helps those who ask for his help, after the steamer’s having become nothing more than “a single fading light on the blackness of the waters and a dark shadow against the paler sky,” the ship seems to stop so that it might return. His prayer, it seems, has been answered. God, it appears, has heard him, and “a surge of joy and hope” flashes “through his mind” as he gives thanks to the deity.
A moment later, his hopes are dashed, and he despairs as he sees the ship’s light become “gradually but steadily smaller,” and, where, before, he’d given voice to his gratitude, he now curses his fate: “Beating the water with his arms, he raved impotently. Foul oaths burst from him, as broken as his prayers--and as unheeded.” It seems clear that, whether he pleas for deliverance, gives thanks, or curses God, neither nature nor its Creator hear or respond. They are as indifferent to his gratitude as they are to his need and his thanksgiving. As he becomes exhausted, his “passion” gives way to “fear,” and after only “twenty minutes” have “passed,” he resigns to his fate. Rather than attempt to “swim all the way to Suez,” he decides to drown, and he throws “up his hands impulsively,” sinking, only to find that his instinct to survive takes over, preventing him from committing suicide:
Down, down he went through the warm water. The physical death took hold of him and he began to drown. The pain of that savage grip recalled his anger. He fought with it furiously. Striking out with his arms and legs he sought to get back to the air. It was a hard struggle, but he escaped victorious and gasping to the surface.
He has fought the sea and won. Nature has been vanquished. Even without God’s help, he has managed to escape the “savage grip” of “physical death,” but his is a short-lived, hollow victory, for, as he bursts through the surface of the water, “despair awaited him.” He realizes that it is futile for him to struggle, that his fate is sealed. He pleads, once more, to God, praying, “Let me die.”
The narrator describes the appearance of a shark, a maritime angel of death, as it were, as beautiful and awesome as any other terrible messenger of God. The creature’s beauty seems, from a human perspective, incongruous and inappropriate, but the story is being told from the omnipotent point of view, as if it were God himself who tells the tale of the man overboard, and human attitudes are irrelevant. As the moon drifts out from the cover of the night’s cloud, symbolizing divine revelation, an epiphany occurs, for the reader, if not for the man overboard, courtesy of the narrator’s concluding observation concerning the significance of the shark’s appearance:
The moon, then in her third quarter, pushed out from the concealing clouds and shed a pale, soft glimmer upon the sea. Upright in the water, fifty yards away,was a black triangular object. It was a fin. It approached him slowly.
His last appeal had been answered.
Significantly, it is the man’s “last appeal” that has “been answered.” He had made an earlier appeal, praying that God would deliver him, but those pleas had fallen, as it were, upon deaf ears. Only his prayer that he be allowed to die is answered. He will be allowed to die, but not by drowning. Instead, he will be ripped apart, alive, and devoured. The moon, shedding the light of revelation, as it were, upon this final incident of the story, suggests that, if God is not altogether indifferent to man’s fate, he is, if anything, a sadist.
Just as the ship is a synecdoche for technology; music, for art and the pleasures it brings; the mail, for human contact and communication; and the sea, for nature itself, the anonymous man is a synecdoche for humanity itself. Not only is the nameless, faceless man of the story alone and abandoned by God in an uncaring and impersonal universe which is equally indifferent to the man’s happiness and welfare, but, in him, all humanity is overboard, awash in a sea of cosmic unconcern and disregard.
Is the tone of the story (and, therefore, of the narrator’s final observation, that “his last appeal had been answered”) sincere, ironic, or cynical? There is some ambiguity in the story’s wording, as there is in its structure and its incidents--and enough uncertainty, perhaps, to make all three interpretations of the tone possibilities. The answer to the question of whether the tone is ultimately sincere, ironic, or cynical is up to each reader to decide, and his or her answer will be determined by the views that he or she holds concerning nature and its Creator.
The Christian might consider the shark’s appearance, in answer to the man’s prayer that he be allowed to die, to be a sincere response on the part of God; the Deist might suppose the shark’s appearance to be mere coincidence, since God, although he exists and did create the universe, takes no current interest in his creation; the atheist might consider the shark’s appearance also a matter of nothing more than mere blind chance, since there is no God to hear or respond to the man’s--or anyone else’s--prayer.
The story is marvelously short, just as it is marvelously uncanny. Despite its brevity, it presents amazingly complex questions concerning the character of nature, the problem of evil, and the nature of God. Although one opinion concerning the story’s tone and the narrator’s final observation may seem more likely than others, each remains a possibility, and God may not be the sadist he at first appears to be. Death by shark would be horrible, to be certain, but would drowning be any quicker, more merciful, or dignified? On the other hand, if God exists, maybe he is as capricious and even as sadistic as the story can be interpreted to imply. For that matter, why did the man fall overboard?
To universalize the question, we might ask, instead, Why did humanity, in the Garden of Eden, take a similar fall? Is there a grace behind both “falls,” discernable only to the eye of faith, as Job suggests? Is the fall overboard a test of one’s trust in God, even when one faces his own mortality? Is the story a repudiation of the very idea of a merciful and loving God? Is he, instead, merely just and inscrutable? Does he exist at all?